Overview
The Rheumatology Department specializes in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal diseases and systemic autoimmune conditions, commonly referred to as rheumatic diseases. These disorders can affect joints, muscles, bones, and other tissues, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and potential deformities. Rheumatologists work closely with patients to manage chronic conditions, improve quality of life, and prevent long-term complications through a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
TREATMENTS & PROCEDURE

Comprehensive assessment and treatment strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatologists provide personalized care for rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting joints. Treatment involves medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes to reduce symptoms and prevent joint damage.
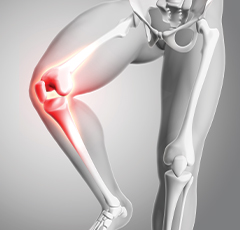
Strategies to manage and relieve symptoms of osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis management includes medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to reduce joint pain and stiffness. Emphasis is placed on maintaining joint function and improving mobility.
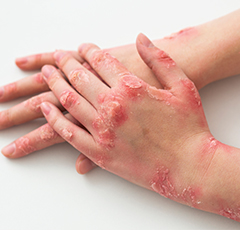
Tailored treatment plans for managing systemic lupus erythematosus.
Treatment for lupus involves medications to control the immune system, reduce inflammation, and manage symptoms. Regular monitoring and adjustments in therapy are crucial for disease management.
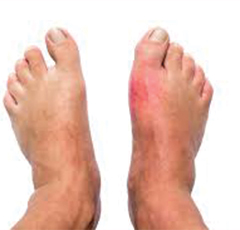
Effective strategies to prevent and treat gout flare-ups.
Gout management focuses on reducing uric acid levels through medications and dietary changes to prevent flare-ups and joint damage. Acute attacks are treated with anti-inflammatory drugs.

Comprehensive treatment for the systemic effects of scleroderma.
Scleroderma care includes medications to manage skin thickening and organ involvement, as well as therapies to maintain function and quality of life. Regular monitoring is essential for managing disease progression.

Specialized care to manage spinal inflammation and improve quality of life.
Treatment for ankylosing spondylitis involves medications, physical therapy, and exercise to reduce spinal inflammation, enhance mobility, and alleviate pain. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to preventing complications.
Comprehensive assessment and treatment strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis.

Rheumatologists provide personalized care for rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting joints. Treatment involves medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes to reduce symptoms and prevent joint damage.
Strategies to manage and relieve symptoms of osteoarthritis.

Osteoarthritis management includes medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to reduce joint pain and stiffness. Emphasis is placed on maintaining joint function and improving mobility.
Tailored treatment plans for managing systemic lupus erythematosus.

Treatment for lupus involves medications to control the immune system, reduce inflammation, and manage symptoms. Regular monitoring and adjustments in therapy are crucial for disease management.
Effective strategies to prevent and treat gout flare-ups.

Gout management focuses on reducing uric acid levels through medications and dietary changes to prevent flare-ups and joint damage. Acute attacks are treated with anti-inflammatory drugs.
Comprehensive treatment for the systemic effects of scleroderma.

Scleroderma care includes medications to manage skin thickening and organ involvement, as well as therapies to maintain function and quality of life. Regular monitoring is essential for managing disease progression.
Specialized care to manage spinal inflammation and improve quality of life.

Treatment for ankylosing spondylitis involves medications, physical therapy, and exercise to reduce spinal inflammation, enhance mobility, and alleviate pain. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to preventing complications.
FAQs
A rheumatologist diagnoses and treats musculoskeletal diseases and systemic autoimmune conditions, managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Treatment involves medications (DMARDs, biologics), physical therapy, and lifestyle changes to reduce inflammation and prevent joint damage.
Lupus is managed with immunosuppressive drugs, corticosteroids, antimalarials, biologics, and lifestyle modifications to control autoimmune activity and symptoms.
Treatments include immunosuppressive drugs, vasodilators, physical therapy, pain management, skin care, and organ-specific therapies.
Conditions include rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, lupus, gout, scleroderma, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis.
Management includes NSAIDs, physical therapy, joint injections, weight management, and assistive devices to reduce pain and improve joint function.
Gout management focuses on reducing uric acid levels through medications and dietary changes, with acute attacks treated using anti-inflammatory drugs.
Treatment involves NSAIDs, TNF inhibitors, physical therapy, exercise, pain management, and posture training to manage spinal inflammation and improve mobility.
Rheumatology Doctors


